
연세대학교 박종혁 교수(화공생명공학과) 연구팀은 카본나노튜브-PVDF 바인더 복합체와 에칭된 알루미늄 집전체를 활용한 신규 건식 전극 공정을 통해 고로딩·고성능의 건식 전극을 개발했다. 이번 연구는 리튬이온전지의 제작 비용 절감과 지속가능성에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대되며, 전 세계적으로 높은 관심을 받고 있는 건식 전극 공정의 새로운 지표를 제시했다는 점에서 의의가 있다.
연구팀은 카본나노튜브와 PVDF 바인더를 혼합한 건식 복합체를 에칭된 알루미늄 집전체에 핫 프레스 방식으로 부착했을 때 매우 강한 접착성을 갖는다는 것을 발견하고, 이를 전극 스캐폴드로 활용하는 건식 공정인 ‘드라이 프레스 코팅(Dry press-coating)’ 공정을 새롭게 고안했다. 이 공정으로 만들어진 전극은 카본나노튜브들이 서로 강하게 엉켜 있는 구조적 특징을 갖고 있어 활물질을 전극 내부에 단단하게 붙잡고 동시에 벨크로 테이프처럼 에칭된 집전체 기공들에 고정돼 매우 높은 응집력(Cohesion)과 접착력(Adhesion)을 갖는다.
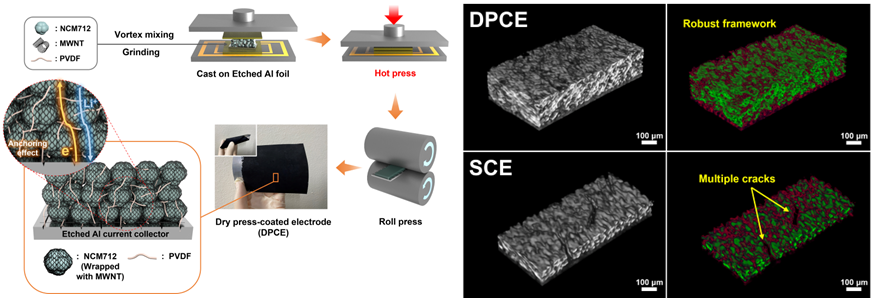
이러한 특성으로 인해 로딩이 높아질수록 구조가 촘촘해져 응집력과 접착력이 증가했고, Micro-CT를 통해 습식 전극과 비교했을 때 월등히 뛰어난 구조적 안정성을 보였다. 습식 전극과 동일 조건에서 전기화학적 성능을 비교해 봐도 우월한 수명 안정성과 율속 성능을 보였으며, 테스트가 끝난 전극 분석에서도 전이 금속 석출량과 전해질과의 부반응이 현저하게 적은 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
더불어, 고로딩 건식 전극을 리튬 메탈 파우치 셀에 적용했을 때, 높은 전류 밀도 조건에서도 첫 사이클에서 양극 이론 용량의 98%가 발현되고, 100 사이클 후에도 85%의 용량 유지 성능을 보이는 것을 확인했다. 최종적으로, 연구팀은 전극 로딩을 최대치로 높인 초고로딩 건식 전극을 이용해 고에너지 밀도 리튬 메탈 파우치 셀을 구현함으로써 건식 전극의 실질적인 상업화 가능성을 선보였다.
연세대 박종혁 교수는 “이번 연구는 개발 단계에서 고전하고 있는 건식 공정의 고질적인 문제점을 개선하고 건식 공정의 상업화에 한걸음 더 나아갈 수 있는 방법을 제시했다”며, “개발한 건식 공정은 전고체 전지용 전극 제작에도 활용할 수 있기 때문에 차세대 전고체 전지용 건식 전극 개발을 목표로 후속 연구를 진행 중”이라고 전했다. 이 연구는 한국연구재단 지원으로 박종혁 교수 연구팀의 류민제 연구원 (제 1저자)과 함께 진행됐으며, 국제 학술 권위지인 ‘네이처 커뮤니케이션즈(Nature Communications)’에 3월 10일 게재됐다.
A research team led by Professor Jong Hyeok Park from Yonsei University's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed a new dry electrode process that utilizes a multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWNT) - polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) binder composite as a conductive scaffold for active materials, and an etched aluminum (Al) foil as a current collector. This research presents a new index for the dry electrode process, which is expected to lower manufacturing costs and enhance the sustainability of lithium-ion batteries.
The research team found that a dry composite mixture comprised of MWNT and PVDF binders has strong adhesion when attached via hot pressing to an etched aluminum current collector. Based on this finding, the team devised a new "dry press-coating" process that uses MWNT-PVDF composite it as an electrode scaffold and an etched Al foil as a substrate. The electrode made using this process has a structure in which carbon nanotubes are strongly entangled, holding the active material inside the electrode layer while also being fixed to etched current collector pores, resulting in high cohesion and adhesion.
Due to these characteristics, as the loading increased, the structure of dry electrode became denser and more concrete when compared to wet electrodes. Micro-CT analysis also confirmed more robust and superior structural stability of the dry electrode compared to the wet electrode. Additionally, the electrochemical performance tests demonstrated that the dry electrode exhibited superior cyclability and rate performance compared to the wet electrode. Moreover, the post-mortem analysis revealed that the dry electrode incorporated cell had remarkably low amount of transition metal dissolution and side reaction between electrolytes.
In addition, when the high loading dry electrode was fabricated and applied to a lithium metal pouch cell, 98% of the cathode theoretical capacity was realized in the first cycle, and 85% was maintained after 100 cycles even under high current density condition of 0.5 C. Finally, the research team presented a high energy density(360 Wh/kg and 701 Wh/L) lithium metal pouch cell using an ultra-high loading dry electrode with a maximum electrode loading of 100 mg/cm2.
Professor Jong-hyeok Park of Yonsei University said, "This study presented a novel approach to overcome the challenges faced by current dry process techniques and could potentially be used in all-solid-state battery electrode fabrication processes."
The work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant by the Korean Government (MSIT). This research was conducted by Minje Ryu (first author) and was published online on March 10 in the international academic journal of ‘Nature Communications, (IF:17.694)’.
Nature Communications (2023) (IF: 17.694)
Published: March 10, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37009-7